-
ABOUT US
-
R&D
-
AGORA
-
PR
-
RECRUITMENT
-
CONTACT
R&D
3HOTP
What is 3HOTP?
- 3H Bio Co., Ltd., has developed a highly effective anti-obesity vaccine, 3HOTP, that can be administered safely for the whole life.
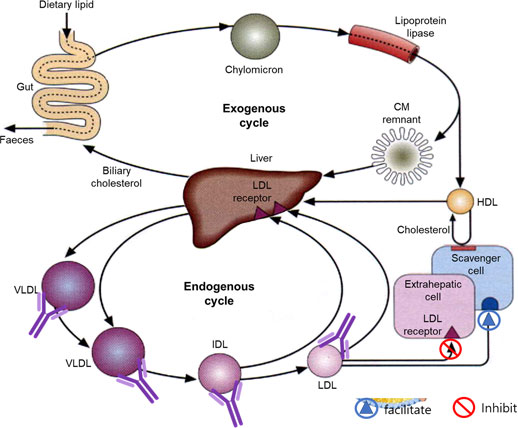
- 3HOTP is directed against ApoB100, a naturally occurring protein that is an essential component of the lipoproteins, VLDL, IDL, LDL.
- Effective obesity treatments must affect energy intake, absorption, expenditure, or storage. The new 3HOTP works by increasing expenditure and reducing storage.
- When vaccinated mature male mice were given a high-fat diet, they ate normally, yet gained less weight and had less body fat.
This shows a way to stop the infamous "yo-yo effect", the cycle of repeated loss and regain of weight that frustrates many dieters.
3HOTP for Human & Animal
-
1. Vaccination
-
2. Stimulation of B cells
-
3. Induction of antibodies
-
4. The induced antibodies bind to ApoB100
Therapeutic principle and approach
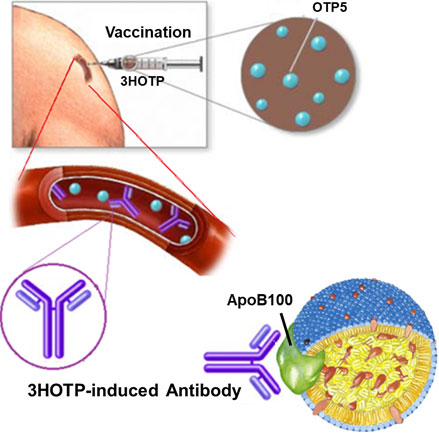
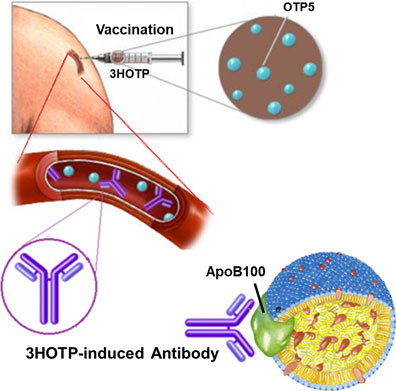
- When 3HOTP is administered, antibodies form that recognize the antigenic peptide OTP5 (the active pharmaceutical ingredient of 3HOTP).
- These antibodies bind to the ApoB100 protein of lipoproteins (VLDL, IDL, LDL).
- The Fab domains (two) of the antibodies bind to the ApoB100 of the fat particles, preventing fat storage in adipocytes.
- The Fc domain (one) of the antibodies promote the phagocytic uptake of the antibody-bound fat particles by macrophages.
Mode of Action I
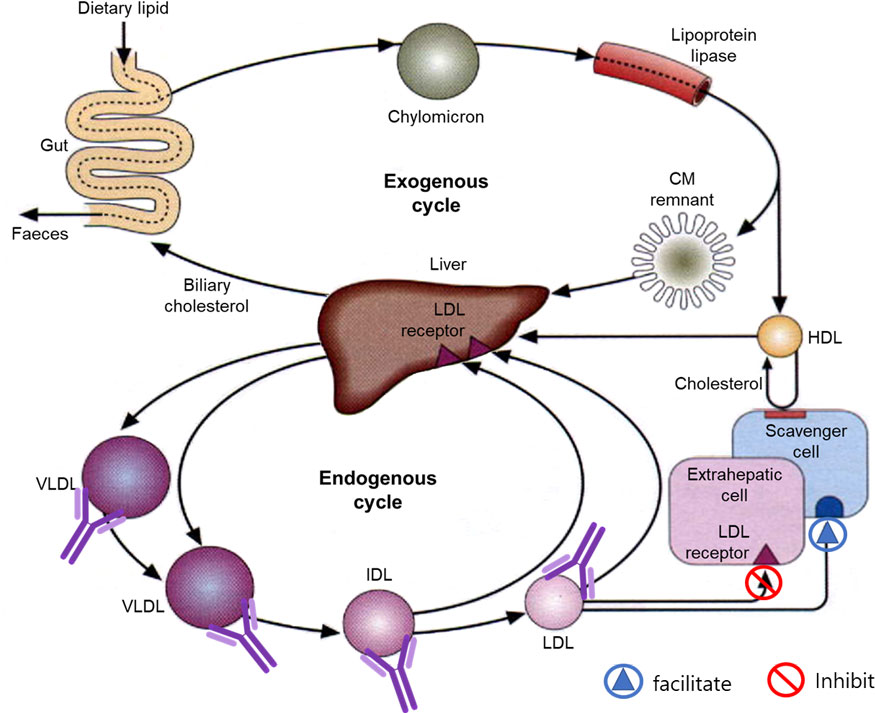
Mode of Action II
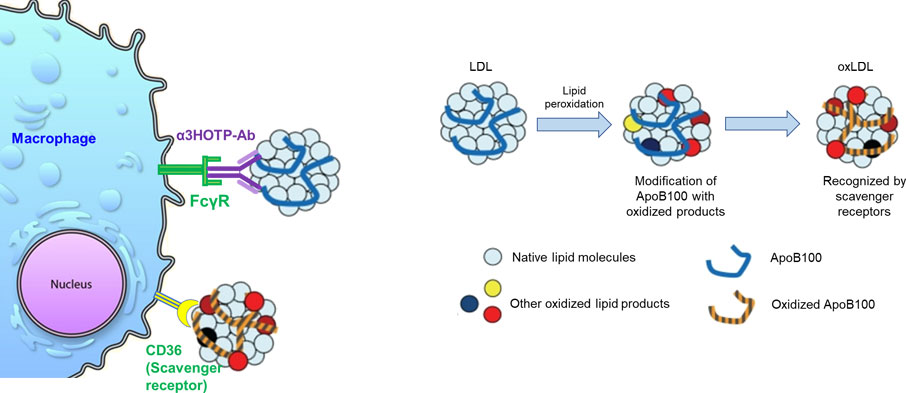
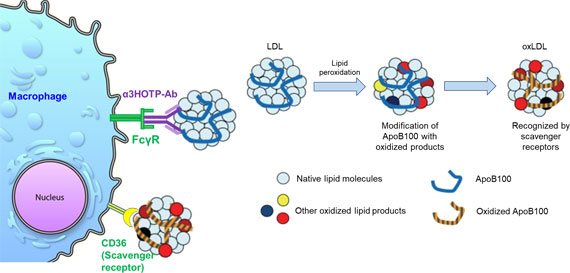
- When LDL is oxidized into oxLDL, it is captured by scavenger receptors of macrophages, transforming them into foam cells (diseased cells).
- However, antibody-bound lipid particles bind to Fc receptors of macrophages before being oxidized, and the lipid particles are absorbed and degraded by macrophages, without converting them into foam cells.
ApoB100 as an immunotherapeutic target
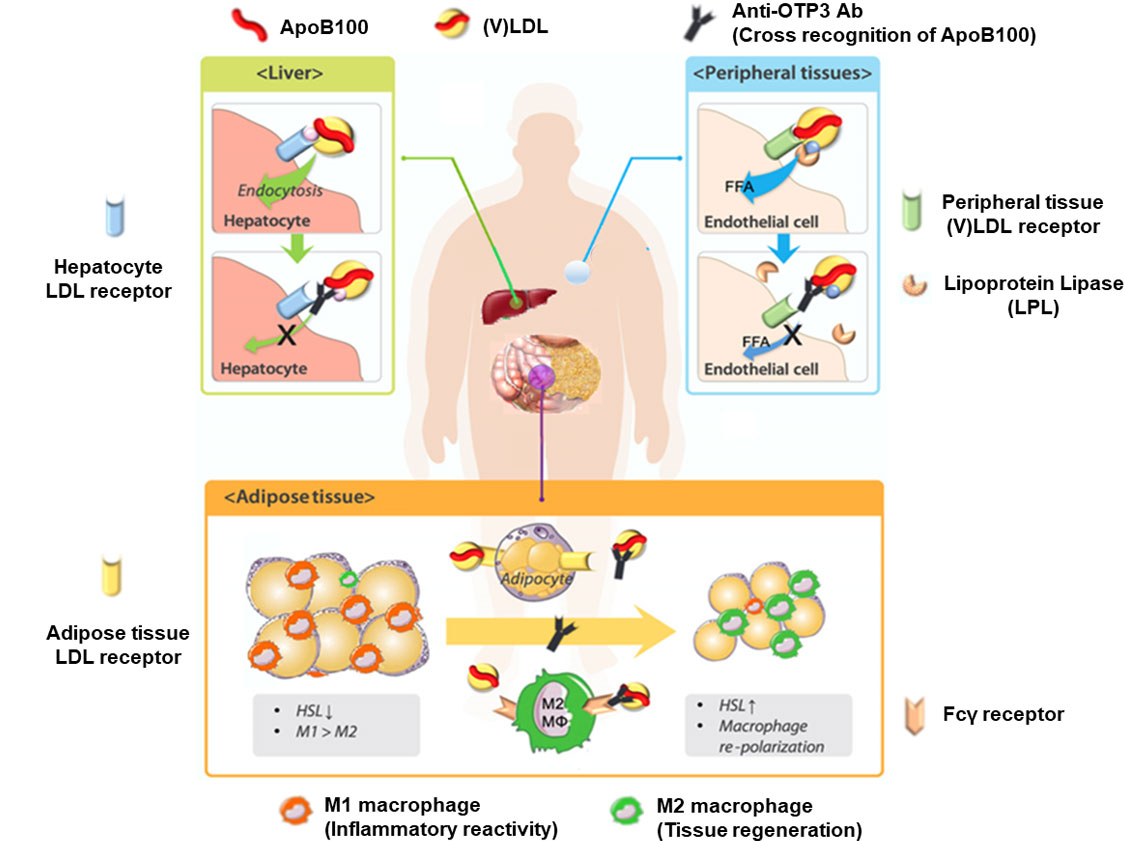
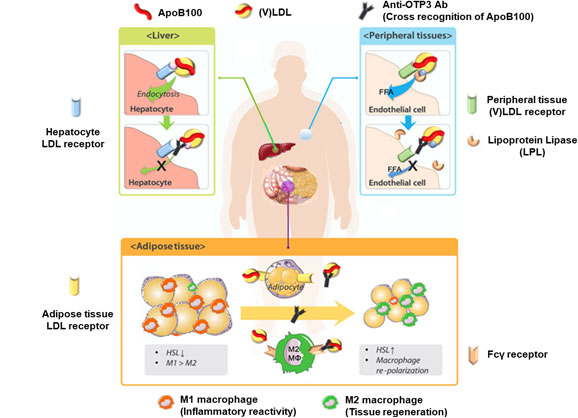
In adipose tissues
- Re-routing of (V)LDL towards macrophages (no foam cells)
- Increased lipolysis
- A less inflammatory environment
In liver
- Blockage of lipid uptake by hepatocytes
Secondary beneficial effects
- Tissue macrophage repolarization towards a non-inflammatory phenotype.
- Prevention of the onset and progression of diet-induced fatty liver, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and most likely atherogenesis.